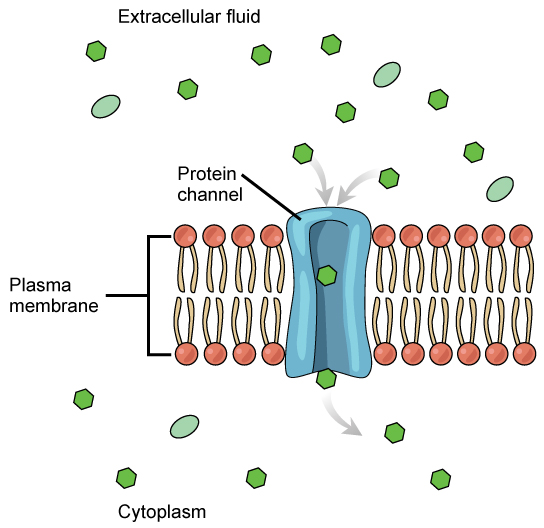
How Are Transport Proteins . membrane proteins come in two basic types: Both form continuous protein pathways across the lipid bilayer. transport proteins play a crucial role in cellular function, enabling the movement of molecules across biological. transport proteins are located in the cell membrane of all cells and are responsible for moving materials into and. Integral membrane proteins (sometimes called intrinsic), which are directly inserted within the phospholipid. there are two classes of membrane transport proteins—carriers and channels. transport proteins or transporter are integral membrane proteins that help other substances to diffuse in. transport proteins in the cell membrane allow for selective passage of specific molecules from the external environment.
from pediaa.com
transport proteins in the cell membrane allow for selective passage of specific molecules from the external environment. membrane proteins come in two basic types: transport proteins play a crucial role in cellular function, enabling the movement of molecules across biological. Both form continuous protein pathways across the lipid bilayer. transport proteins are located in the cell membrane of all cells and are responsible for moving materials into and. transport proteins or transporter are integral membrane proteins that help other substances to diffuse in. Integral membrane proteins (sometimes called intrinsic), which are directly inserted within the phospholipid. there are two classes of membrane transport proteins—carriers and channels.
Difference Between Channel and Carrier Proteins Characteristics
How Are Transport Proteins transport proteins in the cell membrane allow for selective passage of specific molecules from the external environment. there are two classes of membrane transport proteins—carriers and channels. Integral membrane proteins (sometimes called intrinsic), which are directly inserted within the phospholipid. transport proteins play a crucial role in cellular function, enabling the movement of molecules across biological. transport proteins or transporter are integral membrane proteins that help other substances to diffuse in. Both form continuous protein pathways across the lipid bilayer. transport proteins in the cell membrane allow for selective passage of specific molecules from the external environment. transport proteins are located in the cell membrane of all cells and are responsible for moving materials into and. membrane proteins come in two basic types:
From pediaa.com
Difference Between Channel and Carrier Proteins Characteristics How Are Transport Proteins Integral membrane proteins (sometimes called intrinsic), which are directly inserted within the phospholipid. there are two classes of membrane transport proteins—carriers and channels. membrane proteins come in two basic types: transport proteins play a crucial role in cellular function, enabling the movement of molecules across biological. Both form continuous protein pathways across the lipid bilayer. transport. How Are Transport Proteins.
From organismalbio.biosci.gatech.edu
Motor proteins and muscles Organismal Biology How Are Transport Proteins transport proteins or transporter are integral membrane proteins that help other substances to diffuse in. there are two classes of membrane transport proteins—carriers and channels. transport proteins in the cell membrane allow for selective passage of specific molecules from the external environment. Integral membrane proteins (sometimes called intrinsic), which are directly inserted within the phospholipid. transport. How Are Transport Proteins.
From www.vrogue.co
Transporter Proteins Basics Carrier Channel Mediated vrogue.co How Are Transport Proteins Both form continuous protein pathways across the lipid bilayer. transport proteins in the cell membrane allow for selective passage of specific molecules from the external environment. transport proteins are located in the cell membrane of all cells and are responsible for moving materials into and. Integral membrane proteins (sometimes called intrinsic), which are directly inserted within the phospholipid.. How Are Transport Proteins.
From mavink.com
Channel Proteins Vs Transport Proteins Line Graph How Are Transport Proteins transport proteins in the cell membrane allow for selective passage of specific molecules from the external environment. Integral membrane proteins (sometimes called intrinsic), which are directly inserted within the phospholipid. Both form continuous protein pathways across the lipid bilayer. transport proteins or transporter are integral membrane proteins that help other substances to diffuse in. membrane proteins come. How Are Transport Proteins.
From www.cell.com
Protein and RNA Export from the Nucleus Developmental Cell How Are Transport Proteins transport proteins play a crucial role in cellular function, enabling the movement of molecules across biological. Integral membrane proteins (sometimes called intrinsic), which are directly inserted within the phospholipid. transport proteins or transporter are integral membrane proteins that help other substances to diffuse in. transport proteins in the cell membrane allow for selective passage of specific molecules. How Are Transport Proteins.
From www.britannica.com
Membrane Definition, Structure, & Functions Britannica How Are Transport Proteins Both form continuous protein pathways across the lipid bilayer. transport proteins or transporter are integral membrane proteins that help other substances to diffuse in. transport proteins in the cell membrane allow for selective passage of specific molecules from the external environment. membrane proteins come in two basic types: Integral membrane proteins (sometimes called intrinsic), which are directly. How Are Transport Proteins.
From www.pinterest.de
Pin on Anatomy & Physiology How Are Transport Proteins Integral membrane proteins (sometimes called intrinsic), which are directly inserted within the phospholipid. transport proteins play a crucial role in cellular function, enabling the movement of molecules across biological. transport proteins are located in the cell membrane of all cells and are responsible for moving materials into and. transport proteins or transporter are integral membrane proteins that. How Are Transport Proteins.
From commons.wikimedia.org
FileSummary of the protein biosynthesis process.png Wikimedia Commons How Are Transport Proteins Both form continuous protein pathways across the lipid bilayer. there are two classes of membrane transport proteins—carriers and channels. Integral membrane proteins (sometimes called intrinsic), which are directly inserted within the phospholipid. transport proteins in the cell membrane allow for selective passage of specific molecules from the external environment. transport proteins play a crucial role in cellular. How Are Transport Proteins.
From www.peregene.com
What Are Membrane Transport Proteins Transport Informations Lane How Are Transport Proteins membrane proteins come in two basic types: transport proteins play a crucial role in cellular function, enabling the movement of molecules across biological. transport proteins are located in the cell membrane of all cells and are responsible for moving materials into and. Both form continuous protein pathways across the lipid bilayer. transport proteins or transporter are. How Are Transport Proteins.
From phys.org
The yin and yang in the life of proteins Two opposing mechanisms How Are Transport Proteins transport proteins or transporter are integral membrane proteins that help other substances to diffuse in. transport proteins are located in the cell membrane of all cells and are responsible for moving materials into and. transport proteins in the cell membrane allow for selective passage of specific molecules from the external environment. transport proteins play a crucial. How Are Transport Proteins.
From flexbooks.ck12.org
CK12Foundation How Are Transport Proteins Integral membrane proteins (sometimes called intrinsic), which are directly inserted within the phospholipid. transport proteins in the cell membrane allow for selective passage of specific molecules from the external environment. Both form continuous protein pathways across the lipid bilayer. transport proteins or transporter are integral membrane proteins that help other substances to diffuse in. there are two. How Are Transport Proteins.
From www.alamy.com
Cellular protein transport. Proteins are synthesises by ribosomes (blue How Are Transport Proteins transport proteins are located in the cell membrane of all cells and are responsible for moving materials into and. Both form continuous protein pathways across the lipid bilayer. transport proteins play a crucial role in cellular function, enabling the movement of molecules across biological. transport proteins in the cell membrane allow for selective passage of specific molecules. How Are Transport Proteins.
From www.youtube.com
Transport Proteins YouTube How Are Transport Proteins membrane proteins come in two basic types: transport proteins are located in the cell membrane of all cells and are responsible for moving materials into and. Both form continuous protein pathways across the lipid bilayer. Integral membrane proteins (sometimes called intrinsic), which are directly inserted within the phospholipid. transport proteins play a crucial role in cellular function,. How Are Transport Proteins.
From www.dreamstime.com
Transport protein stock illustration. Illustration of machanism 185990485 How Are Transport Proteins Integral membrane proteins (sometimes called intrinsic), which are directly inserted within the phospholipid. transport proteins play a crucial role in cellular function, enabling the movement of molecules across biological. there are two classes of membrane transport proteins—carriers and channels. membrane proteins come in two basic types: Both form continuous protein pathways across the lipid bilayer. transport. How Are Transport Proteins.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Chapter 7 Membrane Structure and Function PowerPoint How Are Transport Proteins transport proteins in the cell membrane allow for selective passage of specific molecules from the external environment. Both form continuous protein pathways across the lipid bilayer. transport proteins play a crucial role in cellular function, enabling the movement of molecules across biological. transport proteins or transporter are integral membrane proteins that help other substances to diffuse in.. How Are Transport Proteins.
From ptbestaribiology.blogspot.com
Biology Pore Protein and Carrier Protein How Are Transport Proteins Both form continuous protein pathways across the lipid bilayer. Integral membrane proteins (sometimes called intrinsic), which are directly inserted within the phospholipid. transport proteins or transporter are integral membrane proteins that help other substances to diffuse in. transport proteins play a crucial role in cellular function, enabling the movement of molecules across biological. there are two classes. How Are Transport Proteins.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Membrane Structure and Function PowerPoint Presentation, free How Are Transport Proteins transport proteins play a crucial role in cellular function, enabling the movement of molecules across biological. transport proteins in the cell membrane allow for selective passage of specific molecules from the external environment. transport proteins or transporter are integral membrane proteins that help other substances to diffuse in. Both form continuous protein pathways across the lipid bilayer.. How Are Transport Proteins.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Membrane Structure and Function PowerPoint Presentation, free How Are Transport Proteins there are two classes of membrane transport proteins—carriers and channels. transport proteins are located in the cell membrane of all cells and are responsible for moving materials into and. membrane proteins come in two basic types: Both form continuous protein pathways across the lipid bilayer. Integral membrane proteins (sometimes called intrinsic), which are directly inserted within the. How Are Transport Proteins.